Feed Formulation (Doing it yourself) Business Plans
CONTENT
- Feed mill
- Factors to be considered before embarking on feed formulation
- Materials need for feed formulation
- Know the nutrient in your feeds
- Formulating the feed
- Pearson square formula
FEED MILL
Feed mill is a department in livestock production that is made up of one or more buildings where feeds are formulated, processed, packaged and send to various livestock farms to meet their animal needs. This is an important branch in the livestock industry, where feeds are being prepared to meet the nutritional requirement of farm animals. Feed mill is of paramount importance, as it contributes about 85% valve to any agricultural based industry that has animal husbandry as its focus.
Feed formulation is the process
of quantifying the amount of feed ingredients needed for a particular animal in
the right proportion.
FACTORS TO BE CONSIDERED
BEFORE EMBARKING ON FEED FORMULATION
·
Age of animal
·
Origin of animal
·
Nutritional requirement of animal
·
Availability of animal
MATERIALS NEED FOR FEED
FORMULATION
·
CARBOHYDRATE [energy sources (COH)]
CARBOHYDRATE [energy sources (COH)]
1. Maize
2. Cassava
3. Rice
4. Yam
·
PROTEIN (including amino acids)
1. Soya bean cake (SBC)
2. Groundnut cake (GNC)
3. Fish Meal
·
CALCIUM
1. Bone meal
2. Oyster shell
3. Periwinkle shell meal
4. Limestone
5. Snail shell
·
FIBERS
1. Wheat offal
2. Palm kernel cake (PKC)
3. Rice bran
4. Soya beans offal
·
MINERALS(supplements/premixes)
1. Salt
2. Lysine
3. Methionine
·
FAT AND OIL (also essential fatty acids)
1. Animal fat
2. Vegetable oil
·
VITAMIN
·
Vitamin supplements/premixes
KNOW THE NUTRIENT IN YOUR
FEEDS
 |
•
Fish meal is the highest quality protein source
commonly available for feed formulation purposes, especially, when is made from
a good quality whole fish.
•
It is also a rich source of energy and minerals
•
Fish meals are highly digestible, highly palatable, good
smell that gives it a welcoming smell.
•
It contains about 65% protein content with 80%
digestibility
•
Its high in LYS, MET (deficient in plant sources)
•
Fish meal also contains 1-2.5% n-6 fatty acids,
essential to many fish and all shrimp
•
If made from byproducts, its quality is not as good
as trawler-caught
•
The only problem observed is its high ash content,
which sometimes result in mineral imbalance
•
It is not used sparingly because of its high cost in
the market.
•
It can be partially replaced by soybean meal and
other animal meals
•
When using Fish Meal, one must remember that it
cannot be stored forever
•
It can rancidify due to high lipid content
•
further, not all Fish Meal is created equal
•
some types (menhaden) appear to be superior to
others (sardine meal)
•
Fish Meal must be very well ground and sieved to
help remove indigestible parts
Soybean Meal (SBM)
•
Soybean meal has one of the best essential amino
acid profiles of all protein-rich plant feedstuffs
•
Soybean Meal does not appear to be deficient in any
EAA for catfish
•
Soybean Meal can be deficient, because their MET/CYS
requirement is twice that of catfish
•
some fish find Soybean Meal unpalatable, for this
reason maximum levels are suggested
•
Soybean meal is commonly used as a substitute for
fish meal, however, is only to a point
•
shrimp will consume high Soybean Meal feeds, but
diet must be supplemented with fish meal at some point
•
another problem involves losses in energy, minerals
and lipids in diets where Soybean Meal replaces Fish Meal or other animal
byproduct proteins
•
Another variety of soybean meal is known as
“de-hulled”
•
de-hulled soybean meal contains 25% less ME, 85%
less available P and 90% less n-3 FA’s than anchovy meal
•
soybeans also contain trypsin-inhibitors
•
trypsin inhibitor reduces digestibility of soy
protein by the enzyme trypsin
•
solution:
most soybeans are roasted prior to milling (destroys inhibitor)
Full-fat Soybeans
•
Full
fat soybean meal is different from regular Soybean Meal in that it has a full fat complement
•
Full
fat Soybean has not been solvent
extracted
•
Full fat Soybean often used as an energy source or for general balancing of
the formula
•
mainly
used in salmonid (cold water) fish diets
Grains and By-products (carbohydrate → COH)
•
Grains
are primarily used as COH sources
•
when
whole, they contribute about 62%-72% of dietary starch
•
starches
are fairly well digested by warm-water species (60-70%), but not by cold
•
heating
COH via extrusion improves digestibility by 10=15%
•
COH
can also be used as binding agents
•
Corn
is commonly used in the U.S., but is high in xanthophyll (a pigment), giving
tissue a yellow color (not good for fish sales!)
•
corn
gluten meal is high in protein (60%) and contains high levels of MET (excellent
for formulation)
•
rice
bran often used in developing countries due to local rice production
•
rice
bran is a reasonable COH source, but is high in fiber and fat
•
wheat
gluten is a good protein source, but too expensive, often used as a binder
Animal By-products
•
Meat and bone meal is a byproduct of the slaughter
house
•
contains 50-55% crude protein
•
protein quality is low, so only marginally useful
and varies dependent upon meat source
•
can be a good source of energy, P, TM’s
•
another problem:
high ash content
•
digestibility improved by flash- or spray-drying
•
poultry by-product meal (PBM) is often used by mills
also producing chicken feed
•
feather meal high in protein, but indigestible
Crustacean Meals
•
Shrimp waste meal is a reasonably good feed
ingredient, if heads are included
•
otherwise, the shell is primarily chitin and of
limited digestibility
•
the ammonia in chitin accounts for about 10-15% of
the nitrogen in whole meal
•
also a reasonable source of n-3 fatty acids,
cholestrerol and astaxanthin (carotenoid)
•
highly palatable and often serves as an attractant
in feeds at 1-2%
•
others: krill
meal, Artemia meal
Fats and Oils
•
Used as energy sources, provide essential fatty
acids, attractant, coating of pellet to reduce abrasion
•
both animal and plant fats can be used, animal fats
cheaper, better attractants
•
marine lipids often added as oils if FM level is low
(otherwise no source of marine FA’s)
•
sources:
menhaden, shark, cod liver
•
must be careful in storage of oil, feeds with oils
due to rancidification
Fibrous Feedstuffs
•
Most monogastric animals (e.g., fish) do not digest
fibrous feedstuffs well
•
it is unlikely that adding fiber to diets already
with more than 3-5% will have any beneficial effect
•
high fiber content reduces binding capacity of
feeds, inhibits intake (due to reduced palatability), increases rate of passage
and waste production
•
sources:
brans
Binding Agents
• Binding agents are really needed for pelletized feeds, but not necessarily for extruded feeds (we discuss this later)
•
in extruded feeds, all ingredients are gelatinized
by high temperature and bind together well as a result of the process
•
most organic binders are good for about 30 min of
submergence
•
starch is often used at over 10%, however it will
hydrate and swell the pellet
•
chemical binders (e.g., Basfin) have good binding
potential, form cross-linkages with COH and PRO, but are toxic
Basic Facts
•
In addition to the essential nutrients, feeds may
contain organic and inorganic materials that have various effects on aquatic
species:
•
beneficial, detrimental or negligible
•
they can affect growth, health or the processed
product
•
may be naturally occurring, intentionally or
unintentionally added
•
can be produced via microbial growth
Toxins and Antimetabolites
•
The more important toxins affecting animal feeding
are those associated with molds
•
these are called “mycotoxins”
•
three important genera are Aspergillus, Penicillium
and Fusarium
•
they exist and grow anywhere as long as there is
enough COH substrate, no less than 14% moisture, adequate temperature, oxygen
•
usually produced in feedstuffs prior to harvest, but
also result from poor storage
Aflatoxin
•
Aflatoxin is the mycotoxin of greatest concern in
feeding of culture species
•
both outright toxic and carcinogenic
•
liver (hepatoma) and blood clotting problems
•
rainbow trout are highly sensitive at 1 ug/kg
exposure
•
traditionally, sources include corn, cottonseed and
peanuts
•
aflatoxin contamination varies year to year
Ochratoxin
•
These are compounds produced by Aspergillus and
Penicillium molds
•
widely found in nature
•
typically associated with kidney toxicity
•
toxic level is 4.7 mg/kg in diet
•
other mold toxins have been found in warm-blooded
animals, but not in fish
•
most mold toxins also destroy nutrients in feeds
•
example: Pseudomonas
can separate glutamic acid from folic acid, making it ineffective
Microbial Toxins in Commercial Fish/shrimp Feeds
•
Usually not known that the feed is contaminated
•
commercially-processed feeds are less likely to have
these toxins
•
screened against international transport and by feed
manufacturers by law
•
must contain less than 20 ppb
•
up to manufacturer to require testing
•
not destroyed by steam pelleting or extrusion
•
presence in feeds reduced by proprionic acid
Histamine
•
This is a toxic compound found in fish meal, a
typical feed ingredient
•
results from bacterial removal of COOH (carboxylic
acid) from the EAA histidine
•
comes from improper storage of raw fish prior to
production of fish meal
•
causes a reduction in growth rate
•
usually comes from “dark” meat portion of fish
•
other fish meal toxin is “gizzerosine”
Phytic Acid, Gossypol
•
Phytic acid is an organic molecule related to
inositol
•
integral component of plant feedstuffs and holds
60-70% of the phosphorus
•
problem is, it’s poorly available to fish
•
reduces availability of zinc
•
“Gossypol” is a component of pigment lands in the
cotton plant
•
limits availability of cottonseed meal used in feeds
(suppresses growth rate and causes liver damage)
Fish Oils, Fiber
•
Marine fish oils contain 20-25% PUFA’s
•
the “autoxidation” of PUFA’s results in formation of
large numbers of free radicals and peroxide compounds
•
these are toxic due to reaction with other
nutrients, limiting availability
•
also cause cellular/subcellular damage
•
severity of effect reduced by Vit E
•
fiber can also be mildly “toxic” as it increases
rate of gut passage
•
high rate of passage causes reduced availability of
nutrients
Diet Additives:
Hormones
•
Hormonal control used to produce mono sex cultures
of fish
•
reduces reproduction/increases growth
•
ex. Androgenic steroids (ethyltestosterone) fed to
tilapia fry = 90% males
•
does not work the same on all fish
•
17-alpha-methyltestosterone improves growth and
survival in salmonids
•
andorgenic better than estrogenic
•
used as implants in cattle
Pellet Binders
•
Steam pelleted aquatic feeds, especially those fed
to shrimp, contain binders
•
these are used for improving water stability
(reduced leaching and nutrient loss)
•
two different types:
organic matrix (lignosulfonates or polysaccharides)
•
other type:
chemical compounds (sodium hexametaphosphate)
•
no evidence of detrimental effect on aquaculture
species
Antibiotics
•
Some feeds can be formulated with antibiotics for
treatment of Vibriosis, other bacterial infections
•
Three antibiotics approved in U.S. are
sulfadimethoxine, sulfamerazine and terrymycin (oxytetracycline, OTC)
•
OTC commerically available as “medicated” fish
(shrimp) feed, 1,500 mg/kg
•
Must not feed medicated diets within 14-21 days from
slaughter/harvest (more regulations!)
Attractants
•
Attractants are materials added to feeds to serve as
intake (feeding) stimulants
•
They are cost effective since they cause shrimp/fish
to eat feeds that otherwise would not be attractive (consumed)
•
Facilitates inclusion of by-products
•
Usual inclusion level is around 0.5-1.0 %, largely
due to cost
•
Examples:
krill meal, Artemia meal, fish oils, fish meal
•
Sometimes used to reduce protein content of feed
(but most also feed more frequently)
Antioxidants
•
Oxidation of lipids in feeds or feedstuffs can cause
reduction of the nutritional value of certain lipids and vitamins
•
It can also result in production of toxic free
radicals and peroxides (REM?)
•
Potential for formation of these toxic compounds
reduced by synthetic compounds such as BHA (butylated hydroxyanisole, BHT
(butylated hydroxytoluene)
NUTRITIONAL REQUIREMENTS IN ANIMALS
Different animals need
different nutrients to do well in terms of productivity and body build up.
For example, layers will need much of energy feed
(carbohydrates) to be able to produce more eggs, and a drop in the level of
energy will reduce eggs production. Again, birds like broilers will need much
of body-building feeds (protein) for them to gain weight.
Pigs will need much of fats and oil (palm kernel cake)
and protein, while fishes more of protein feeds
FORMULATING THE FEED
There are many method of feed
formulation in the world, some of these are;
·
Computer based
soft ware feed formulator
This is the newly developed
software use in the formulation of feed for different animal in the world
·
Ruler of thumb
·
Pearson square formula
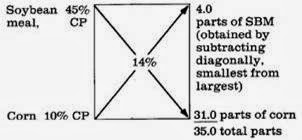
PEARSON
SQUARE FORMULA
This is a universal formula
use in feed formulation. The Pearson square ration formulation procedure is designed
for simple rations. In order for the square to work, follow specific directions
for its use. Nutrient contents of ingredients and nutrient requirements must be
expressed on the same basis (i.e., dry-matter or "as-fed"). The Pearson square or box method of balancing rations is a
simple procedure that has been used for many years. It is of greatest value
when only two ingredients are to be mixed. In taking a close look at the
square, several numbers are in and around the square. Probably one of the more
important numbers is the number that appears in the middle of the square. This
number represents the nutritional requirement of an animal for a specific
nutrient. It may be crude protein or TDN, amino acids, minerals or vitamins.
In order to make the square work
consistently, there are three very important considerations:
.
The value in the middle of the square must be intermediate
between the two values that are used on the left side of the square. For
example, the 14 percent crude protein requirement has to be intermediate
between the soybean meal that has 45 percent crude protein or the corn that has
10 percent crude protein. If barley is used that has 12 percent crude protein
and corn that has 10 percent crude protein, the square calculation method will
not work because the 14 percent is outside the range of the values on the left
side of the square.
2.
Disregard any negative numbers that are generated on the
right side of the square. Be concerned only with the numerical differences
between the nutrient requirement and the ingredient nutrient values.
3.
Subtract the nutrient
value from the nutritional requirement on the diagonal and arrive at a
numerical value entitled parts. By summing those parts and dividing by the
total, you can determine the percent of the ration that each ingredient should
represent in order to provide a specific nutrient level. Always subtract on the
diagonal within the square in order to determine parts. Always double check
calculations to make sure that you did not have a mathematical error. It also
is very important to work on a uniform basis. Use a 100-percent dry-matter
basis for nutrient composition of ingredients and requirements and then convert
to an as-fed basis after the formulation is calculated.
With the rising cost of animal feeds, farmers rearing
animals are increasingly finding it difficult to make profit from their
livestock keeping. All because they find it difficult to formulate their own
feeds for their animals such as poultry birds, catfish, pigs, grass cutters and
so on. Using Pearson Square method, you can easily formulate one now. However,
this is only possible if farmers have the right quality of ingredients or raw
material for formulating feeds. The Pearson Square method relies on the
Digestible Crude Protein (DCP) as the basic nutritional requirement for feed.
The most common ingredients used are whole maize, maize germ, cotton seed cake,
soya beans, sunflower or omena (fishmeal).
Some tips on how to feed chicken
An egg-laying chicken requires 130 g of
feed per day (provide clean water at all times).
• 1 chick requires 2.2 kg of feed for 8
weeks (thus 100 chicks = 2.2 kg x 100=220 kg. Chicks should be allowed to feed
continuously and given adequate clean water at all times). If they finish their
daily rations, you can give the animals fruit and vegetables cuttings to increase
their level of vitamins, minerals and digestion in them.
• 1 pullet (young chicken about to
start laying) should be fed 4.5 kg of feed for two and a half months until the
first egg is seen. It should then be put on layer diet. Supplement with
vegetables, edible plant leaves or fruits peelings in addition to the daily
feed rations.
• All ingredients used must be of high
quality and palatable. Never use rotten maize (Maozo). Chickens are very
susceptible to aflatoxins poisoning.
• When using omena as an ingredient,
ensure it is free of sand and seashells. If
you use maize germ, it should be
completely dry.
• Feed should be thoroughly mixed to
ensure the ingredients are uniformly distributed. It is preferable to use a
drum mixer instead of a spade for mixing.
• Note that even after giving them the
formulated feeds, chickens should be put on free range to scavenge for other
micronutrients not provided for in the feeds.
This is my own resultant on Pearson square formula for layers, using 19.5% crude protein for a 100kg bag.
Carbohydrate
(Energy)
Maize 58.66
Fiber
Wheat offal 14.67
Protein
Soya bean cake 9.23
Groundnut cake 9.23
Blood meal 4.61
Minerals
Premix 0.10kg
Methionine 0.25kg
Salt 0.25kg
Calcium
Bone meal 3kg
Total 100kg bag of feed
For your feed formulation on any animal
OR
WANT'S TO BUY OR SALE YOUR FEED PRODUCTS
Call us, on these numbers;
+2348036925718 +2348051270981
Chris Farm Nigeria develops well self-explanatory, irresistible feasibility studies or business plan for your Business start ups, Business Growth or Expansions through either personal funds, Grants, or loans, which could be new or existing ones. We delight in writing for people under Academic sectors, production sectors, manufacturing sectors, processing or packing sectors, advertising sectors, marketing sectors and other related sectors on mini, middle and large scale businesses.
For your Agribusiness, either production, processing, marketing of any Agro-industry, our feasibility studies or business plan are explicit.
Generally, our feasibility study and business plans are developed so well that it becomes irresistible when you show them to your investors or sponsors. It gives you a clear picture of what you are expected to see when you put the feasibility study or business plans into use. It also shows how much it will cost you to own your desired business, what your money can afford. The kinds of product you will need to minimize input in other to maximize output, and how much returns you will get at the end of each accounting year until your business break-even on its initial investment capital. This will give the intending business person or investor or farmer, a vivid idea on the possible benefit he or she stands to gain, when he or she starts doing the business. With that, the intending business person or investor or farmer will not need a soothsayer to make decision for him or her.
OUR TABLE OF CONTENT INCLUDE;
SECTION 1(Business plan section)
- SECTION I – EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
- NAME OF BUSINESS / COMPANY
- OFFICE & SITE LOCATION
- MOTIVATION
- MISSION STATEMENT
- SOCIAL/ECONOMIC VALUE
- PROJECT STATUS & START UP
- WHY PREPARE THIS BUSINESS PLAN?
- SECURITIES FOR THE PROPOSED LOAN
- REPAYMENT
- SECTION II – STUDY AREA
- STUDY AREA
- COMPANY OVERVIEW
- MANAGEMENT TEAM
- DEPARTMENTS IN THE COMPANY
- EXPERIENCE
- MANAGEMENT TEAM GAPS
- SECTION III – INDUSTRY ANALYSIS
- DEFINING YOUR INDUSTRY
- YOUR INDUSTRY SIZE GROWTH RATE AND SALES PROJECTIONS
- INDUSTRY STRUCTURE
- MARKET OVERVIEW
- MARKET SEGMENTATION
- RELEVANT MARKET SIZE
- KEY SUCCESS FACTORS
- LONG TERM PROSPECTIVE
- MARKET CHARACTERISTICS
- SAMPLING TECHNIQUE
- SECTION IV – CUSTOMER ANALYSIS
- TARGET CUSTOMERS
- CUSTOMER NEEDS
- MARKET NEEDS / SOCIAL PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS
- BUYERS BEHAVIOUR
- MARKET SHARE
- SALES FORECASTING
- SECTION V – COMPETITIVE ANALYSIS
- DIRECT COMPETITORS
- COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGES
- SECTION VI – MARKETING PLAN
- PRODUCTS & SERVICES
- FINISHED PRODUCTS
- PRODUCT QUALITY AND PRODUCTION QUANTITY
- PRODUCTION CAPACITY
- PRICING
- PROMOTIONS PLAN
- DISTRIBUTION PLAN
- SECTION VII – OPERATIONS PLAN
- GENERAL APPROACH TO PRODUCTION
- TECHNICAL ANALYSIS / PRODUCTION PROCESS
- EQUIPMENT
- PACKAGING REQUIREMENTS
- SECTION VIII – FINANCIAL PLAN
- REVENUE MODEL
- FINANCIAL ANALYSIS
- FINANCIAL ASSUMPTIONS
- FINANCE CHARGES
- FINANCIAL PROJECTIONS
- FUNDING REQUIREMENTS/USE OF FUNDS
- CRITICAL ASSUMPTIONS
SECTION 2(Feasibility study section)
- FINANCIAL MODELS
- SUMMARY OF PROJECT COST
- BUDGET OF FIXED ASSETS / CAPITAL EXPENSES / INVESTMENTS
- DEPRECIATION
- UTILITIES
- OPERATING EXPENSES (OPEX)
- TOTAL REQUIRED INVESTMENT OUTLAY (REQUIRED START-UP CAPITAL)
- FINANCING PLAN
- INSTALLED / AVAILABLE EQUIPMENT
- BREAK-EVEN ANALYSIS
- LOAN REPAYMENT SCHEDULE AND INTEREST PAID
- FORECAST OF PROFIT AND LOSS
- CASH FLOW
- BALANCE SHEET
- GENERAL ASSUMPTIONS (BREAK EVEN ANALYSIS)
- BUSINESS RATIOS - PROFITABILITY ANALYSIS
- CONCLUSION
- SECTION 3 – APPENDIX
Click other related clicks that may interest you below;
Acceptable feasibility study and business plan for bank loans
Feasibility study on piggery farming business Agbarho community, delta state
A PREPARED FEASIBILITY STUDY FOR CATFISH FARM IN NIGERIA
“How to own, manage, and make millions from catfish farmingbusiness” BEST SELLER
HOW TO OWN A MEGA FISH FARM BUSINESS IN NIGERIA
FLOATING FISH FEED PELLET MACHINE
TIPS ON BROILERS PRODUCTION AND ACTUAL VACCINATION –PROGRAMME AND TREATMENT
TIPS IN POULTRY MANAGEMENT
Sales of battery cage system in Nigeria
CASSAVA PROCESSING MACHINE
GRASS CUTTER/ CANE RAT PRODUCTION, BEST SELLER
How to handle and manage Snail farming
Rabbit Management
MANAGEMENT OF RABBITS, BEST SELLER
· NOTE; According to our policy, we are not “allowed / permitted” to disclose peoples business or written feasibility study, “to anyone”, irrespective of their personality.
· BUT, WE are permitted to display only executive summary.
· This is just a sample of our executive summary on poultry feasibility study and business plan, carried out in Rivers State.
· 1st sample;
These Feasibility study on poultry farming business (specializing on layers and boilers production), was conducted using projections, impressive publications, compounding interest/values, tables, graph, bar chart, pie chart, profits analysis and cash flow positions in other to give a clear picture of what is obtainable in that location, using eight plots of land, at Esemdiary village, Off Effurun Sapele Road, Okpe LGA of Delta state, Nigeria as a case study.
Esemdiary village is a community in Okpe Local Government Area of Delta State with coordinates 05°26’N 5°57’E, which also plays the host community to the Warri Airport, which is actually located at Osubi.
Okpe Local Government is a territory that used to be part of the original Okpe Kingdom, its headquarters is at Orerokpe, with a population of 128,398 people whose primary occupations include commercial farming, fishing, hunting, trading and gas exploration.
After carrying out the feasibility study on Esemdiary village, Off Effurun-Sapele Road, Okpe LGA of Delta state, Nigeria, it was discovered that, farming generally will do well both on crop and animal production.
HOW TO PLACE AN ORDER NOW?
Payment Methods
Fund Transfer or ATM cash Transfer directly from his/her account into any of CHRIS FARM NIGERIA bank accounts.
If it is an E-Book, project materials, written project or written feasibility study, it will be sent to your immediately as soon as your transaction reflects in our account.
Please note; it will take ten working days to write (or prepare) a feasibility study or a project on your request.
Our bank details are on the website page, Just click on payment to get them
After placing your order, SMS your payment information (Manual title,
Name on teller, payment teller number, and your e-mail address)
E.g. catfish, Kelechi Bisi Amina,531796,allpurpose@yahoo.com
To +2348036925718 or +2348051270981 once I confirm your payment.
The material will be sent to your immediately! By e-mail Trust us 100% to do that.
Advantages of sending your request via email your e-book (electronic book) is downloadable from your e-mail box which allows you to read and print out this book
• Zero shipping costs.
• No wasting time, forget having to wait weeks for postal delivery.
• No risk of products lost in the mail or damaged
Thinking that we might live you after your purchase? Definitely no!
With the CBN policy in Nigeria via bank verification number (BVN), is almost impossible to steal your money from bank transfer or bank payment.
We assure you of maximum support when you need us. Please, do not hesitate to ask us for the way forward.
Get in touch with us today on our phone numbers or send us an email. We await your response……………………….
WRITTEN AND COMPILED BY CHRIS FARM NIGERIA
WEBSITE: www.chrisfarmnigeria.com
EMAIL: chrisfarmnigeria@gmail.com
PHONE: +234(803)-692-5718 or +234(805)-127-0981
LIKE US ON FACEBOOK: www.facebook.com/chrisfarmnigeria
FOLLOW US ON TWITTER: www.twitter.com/chrisfarm9ja
- Bank Deposit
- Electronic Fund Transfer or western money transfer
- ATM cash Transfer
Fund Transfer or ATM cash Transfer directly from his/her account into any of CHRIS FARM NIGERIA bank accounts.
If it is an E-Book, project materials, written project or written feasibility study, it will be sent to your immediately as soon as your transaction reflects in our account.
Please note; it will take ten working days to write (or prepare) a feasibility study or a project on your request.
Our bank details are on the website page, Just click on payment to get them
After placing your order, SMS your payment information (Manual title,
Name on teller, payment teller number, and your e-mail address)
E.g. catfish, Kelechi Bisi Amina,531796,allpurpose@yahoo.com
To +2348036925718 or +2348051270981 once I confirm your payment.
The material will be sent to your immediately! By e-mail Trust us 100% to do that.
Advantages of sending your request via email your e-book (electronic book) is downloadable from your e-mail box which allows you to read and print out this book
• Zero shipping costs.
• No wasting time, forget having to wait weeks for postal delivery.
• No risk of products lost in the mail or damaged
Thinking that we might live you after your purchase? Definitely no!
With the CBN policy in Nigeria via bank verification number (BVN), is almost impossible to steal your money from bank transfer or bank payment.
We assure you of maximum support when you need us. Please, do not hesitate to ask us for the way forward.
Get in touch with us today on our phone numbers or send us an email. We await your response……………………….
WRITTEN AND COMPILED BY CHRIS FARM NIGERIA
WEBSITE: www.chrisfarmnigeria.com
EMAIL: chrisfarmnigeria@gmail.com
PHONE: +234(803)-692-5718 or +234(805)-127-0981
LIKE US ON FACEBOOK: www.facebook.com/chrisfarmnigeria
FOLLOW US ON TWITTER: www.twitter.com/chrisfarm9ja
• A big thank you for your patronage in advance
Your Success, Is Our Optimum Desire
AT Chris farm Nigeria, We Deliver the Best Services…
Other services we render are displayed on our advert below;
ADVERTISEMENT
- We provide feasibility study/business plan for new and existing businesses
- We help you to recruit staff for your company, firm or organizations
- We help you in registering your company, firm or organizations
- Suppliers of any food stuffs
- Building contractor (especially building houses, constructions of ponds)
- Provides Architect for any design
- Help you in getting loans
- Sales of fingerlings, table size catfish, chicks, Grass-cutters, rabbits, snails, and many more
- Farm design
- Feed formulation for general livestock, including
- Floating/Sinking Fish feed
- Soybean oil processing, Teachings on how to test soybean cake,
- Teaching on how to remove the gummy and unpleasant smell of soybean oil
- Palm Oil/Palm nut cracking
- Fish Farming (Pond Construction and Fingerlings distribution)
- Poultry farm (plus marketing ideas)
- Rabbit farming
- Snail Farming
- Grass-cutter/cane rat Farming
- Commercial Crop Farming
- Handwork/Workshop Plan
- Pure Water Business
- Nylon production
- Professional Website design (cooperate and personal)
- Bulk SMS (plus re-seller website)
- Business Software Design
- Logo design plus company slogan
- Printing Press (Graphic design, lithography, banners, poster, handbills etc)
- Sales of battery cage for livestock farming all over Nigeria
- E-books on; Broilers farming, Layers farming, Grass-cutter farming, Rabbit farming, Pig farming, Catfish farming, and many more……
- How to own, manage, and make millions from catfish production (Most demanded)
- Projecting writing, Sales of written projects, and many more…………







Comments
Post a Comment